Help Center - Read Me for Instruction.
EnDisease is a manually curated database for associations of enhancers and diseases based on comprehensive resource paper. Our mission is to provide a curated set of information datasets for the association of enhancers and diseases to support and promote research in this area. Especially, we further provide the causal genes, SNPs information and 871 DNase-seq annotation in every single item, which we believe will be helpful.
Enhancers are short (50-1500 bp) non-coding regions of DNA sequence that enhance the expression of target genes by recruiting regulatory proteins. Active enhancer regions carry particular chromatin marks, and their transcription produces noncoding eRNA. Notably, the eRNA set and corresponding enhancer set show enrichment for variants associated with distinct disorders (Yao et al., 2015).
Although enhancers are among one of the least well-understood elements, emerging studies have revealed that enhancers play critical roles in a broad range of biological processes and are associated with numerous diseases, including cancer (Whyte et al., 2013), cardiovascular disease (Ounzain & Pedrazzini, 2018), and neurodegeneration disorder (Yao et al., 2015). Enhancers are becoming critically important for the understanding of life sciences, especially diseases.
To ensure database quality, we referred to the steps used to assemble other manually curated databases (Li, et al. 2013; Ning, et al. 2015; Guo, et al. 2016). We mainly followed three steps in the data collection process: (1) defining candidate diseases, (2) searching for relevant articles, (3) extracting useful information from the selected articles. First, candidate diseases were defined based on the vocabulary of the OMIM database which contains diseases and disease-related genes information. The candidate enhancers were hard to collect since there are no unified names or symbols for enhancers. Therefore, we only collected 549 diseases terms in the first step. Second, we used a script to automatically select all abstracts in the PubMed database with the following two keywords: (1) a specific disease name (e.g. ‘Crohn’s disease’) (2) ‘enhancer’. Then, we downloaded all published literatures and available supplementary files which describe the associations between diseases and enhancers. Third, we manually extracted experimentally supported enhancer-disease associations from selected articles.
There are 12 columns of every single enhancer-disease interaction which could be access in the Browse and Search page.
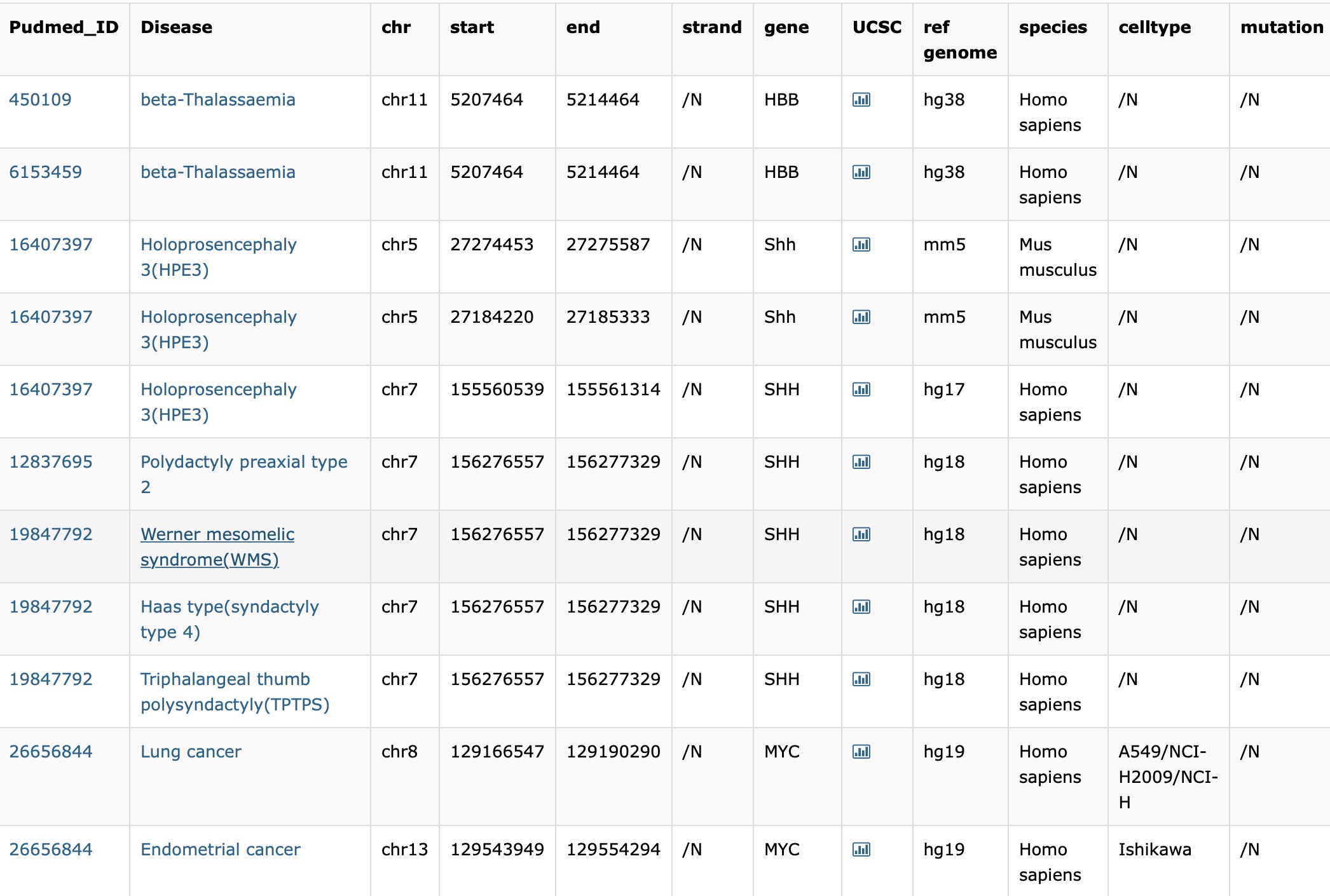
- Pudmed_ID: PubMed ID of original literatures for the enhancer-disease associations and a hyperlink to the literatures in Pubmed.
- chr: The chromatin of the enhancers.
- start: The start site of the enhancers.
- end: The end site of the enhancers.
- strand: The strand of the enhancers.
- gene: The enhancers’ target genes.
- UCSC: A hyperlink to UCSC genome browser to get detailed information of the enhancer regions.
- species: The species where enhancer-disease associations are validated.
- cell type: The cell type where enhancer-disease associations are validated.
- refence genome: The reference genome of the genome coordinate.
- mutation: The mutation information involved in enhancer-disease associations.
- disease: Disease name and a hyperlink to OMIM web page.

Currently, you can:
- browse the experimentally supported enhancer-disease association data;
- search the experimentally supported enhancer-disease association data;
- download the experimentally supported enhancer-disease association data;
We developed EnDisease, an integrated and interactive database of enhancer-disease association, with the primary goal of providing a resource for assistance in further studies related to transcriptional control of cell identity and disease.
In the recent years, disease-associated single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) for autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis have been found to be highly enriched in enhancer regions. The current research well characterized this biological phenomenon and effectively demonstrated the importance and potential application of super-enhancers as they can play key roles in human disease.
EnDisease documents experimentally supported enhancers-diseases associations across different species and annotates each enhancer with 871 DNase-seq experiments in 202 cell types. Our results demonstrate that there are different patterns for cancer-related enhancers and complex disease-related enhancers. EnDisease can serve as a useful resource for researchers who wish to further investigate the mechanisms between enhancers and complex diseases.
Users can browse enhancer-disease interactions with their statistics information and have a glance at the data format and data range of different columns.
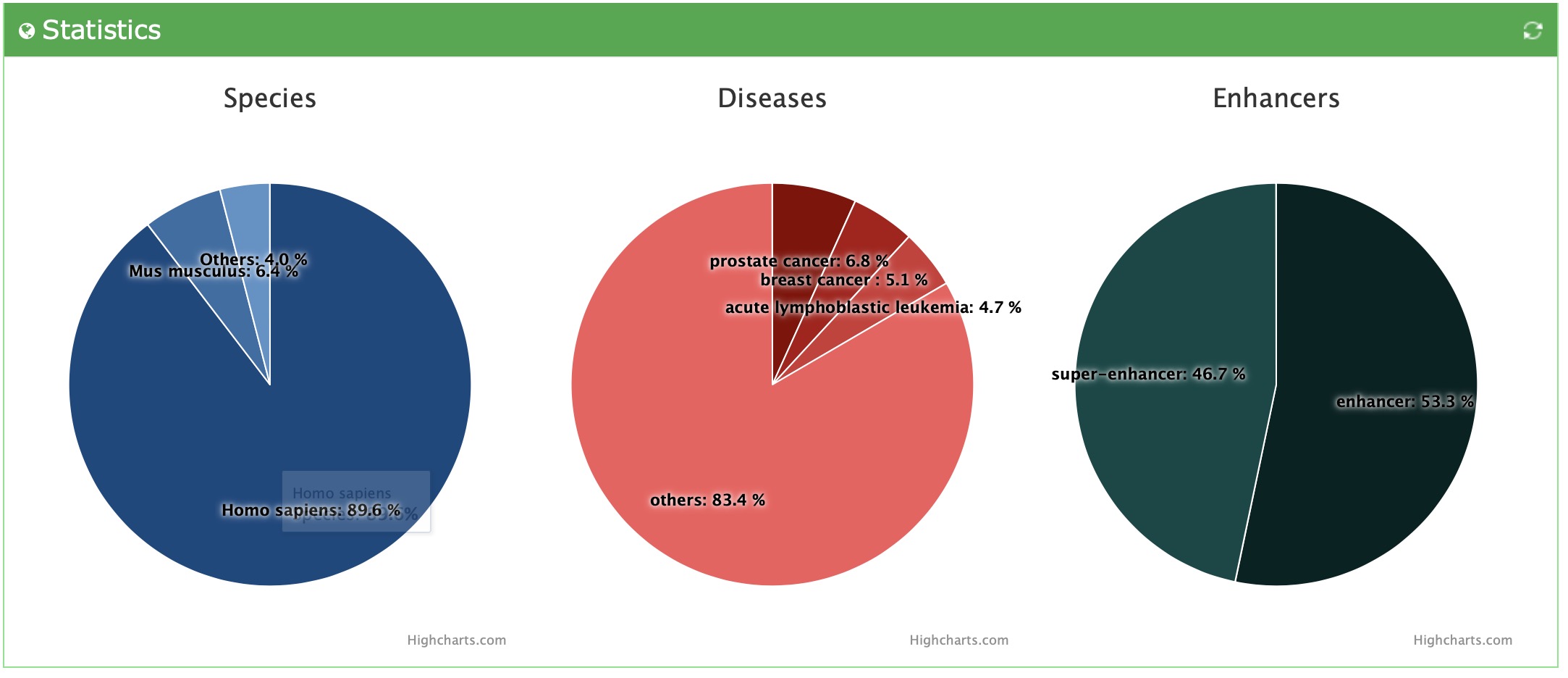
There are three types of statistics results of enhancer-disease interactions, including species, disease and types. We visualize the statistics results using the pie charts and indicate the percentage of different components in the charts.
Users can visualize the enhancer-disease interactions using "browse" module. And we will get the following result:
This is the statistics result of all data:
 And Users can browse the dataset and gain the basic knowledge of the data:
And Users can browse the dataset and gain the basic knowledge of the data:
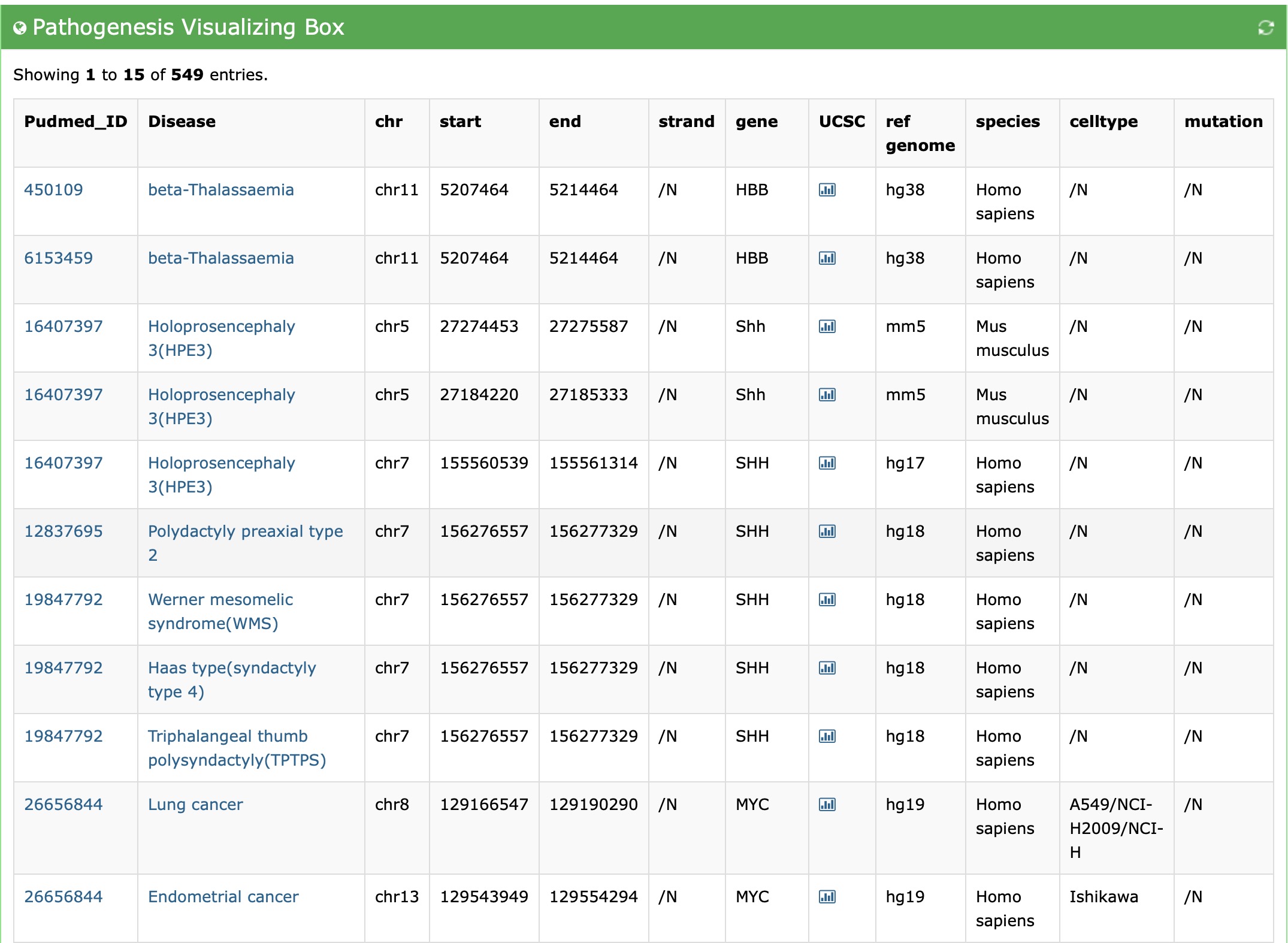
 And Users can browse the dataset and gain the basic knowledge of the data:
And Users can browse the dataset and gain the basic knowledge of the data:

Users can search our database and export what they need.
1."By Enhancer" view
Users can search interactions data according to specific range of genomic position of specific enhancer.
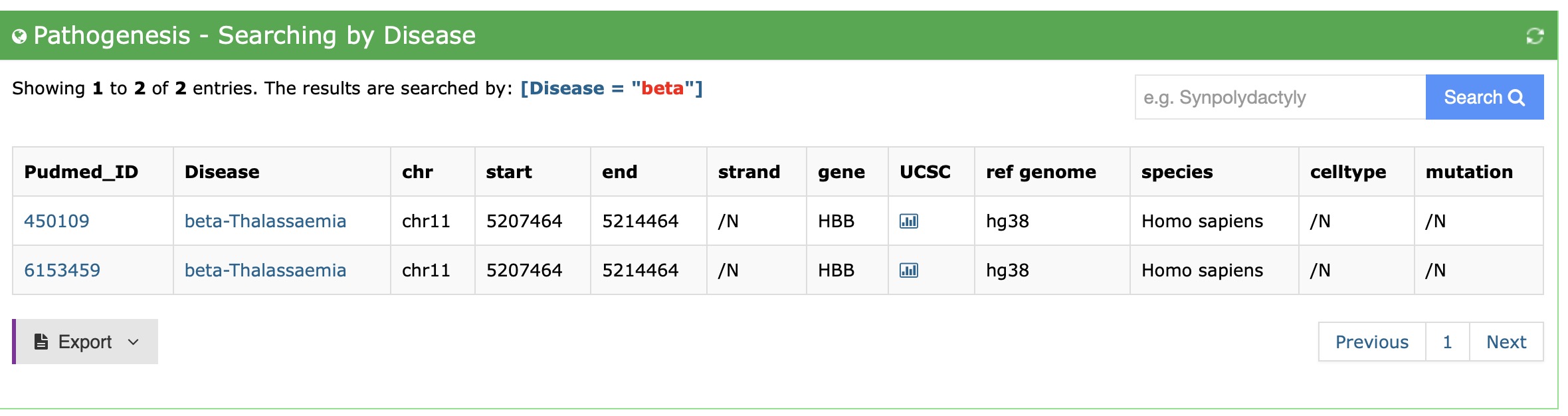
2."By Disease" view
Users can search interactions data according to specific disease.
3."By Gene" view
Users could search interactions data according to specific gene.
4."By Species" view
Users can search interactions data according to specific species.
Users can enter the a chromosome range with chromosome (e.g:chr1), start and end position in the search box in the "By Enhancer" module. Then the database will return some enhancer-disease interactions. The result enhancers are all located within the range. Furthermore, users can export the search result using the export button.
First, enter the chromosome, start position, end position of your interested range:
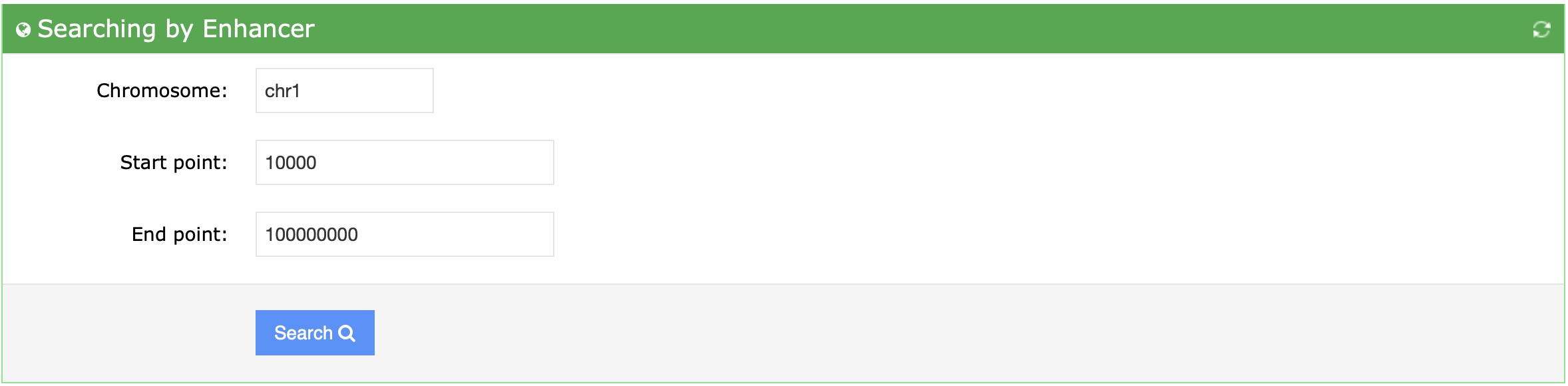 Then you get your result and the search constraint will display at the top:
Then you get your result and the search constraint will display at the top:
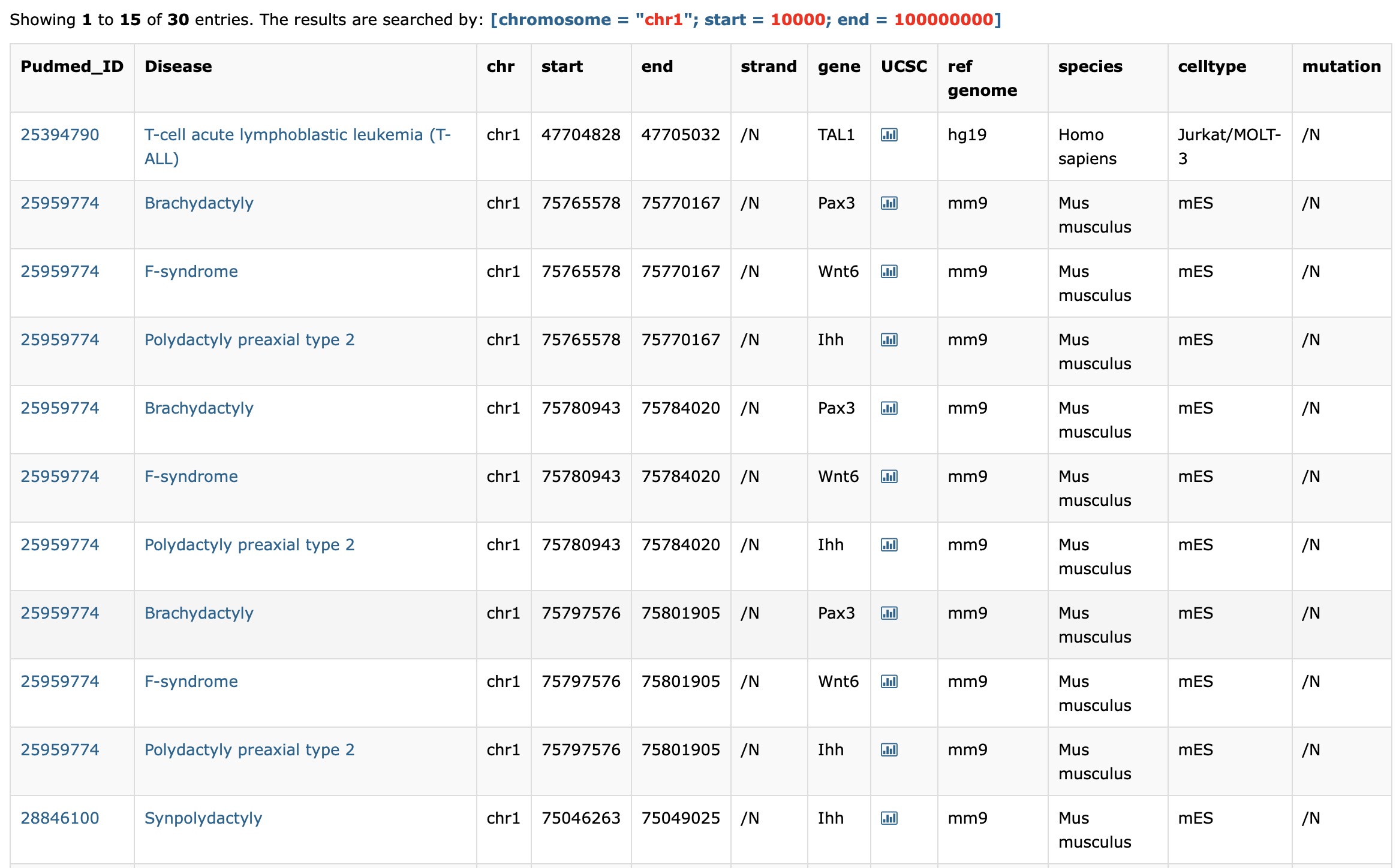
 Then you get your result and the search constraint will display at the top:
Then you get your result and the search constraint will display at the top:

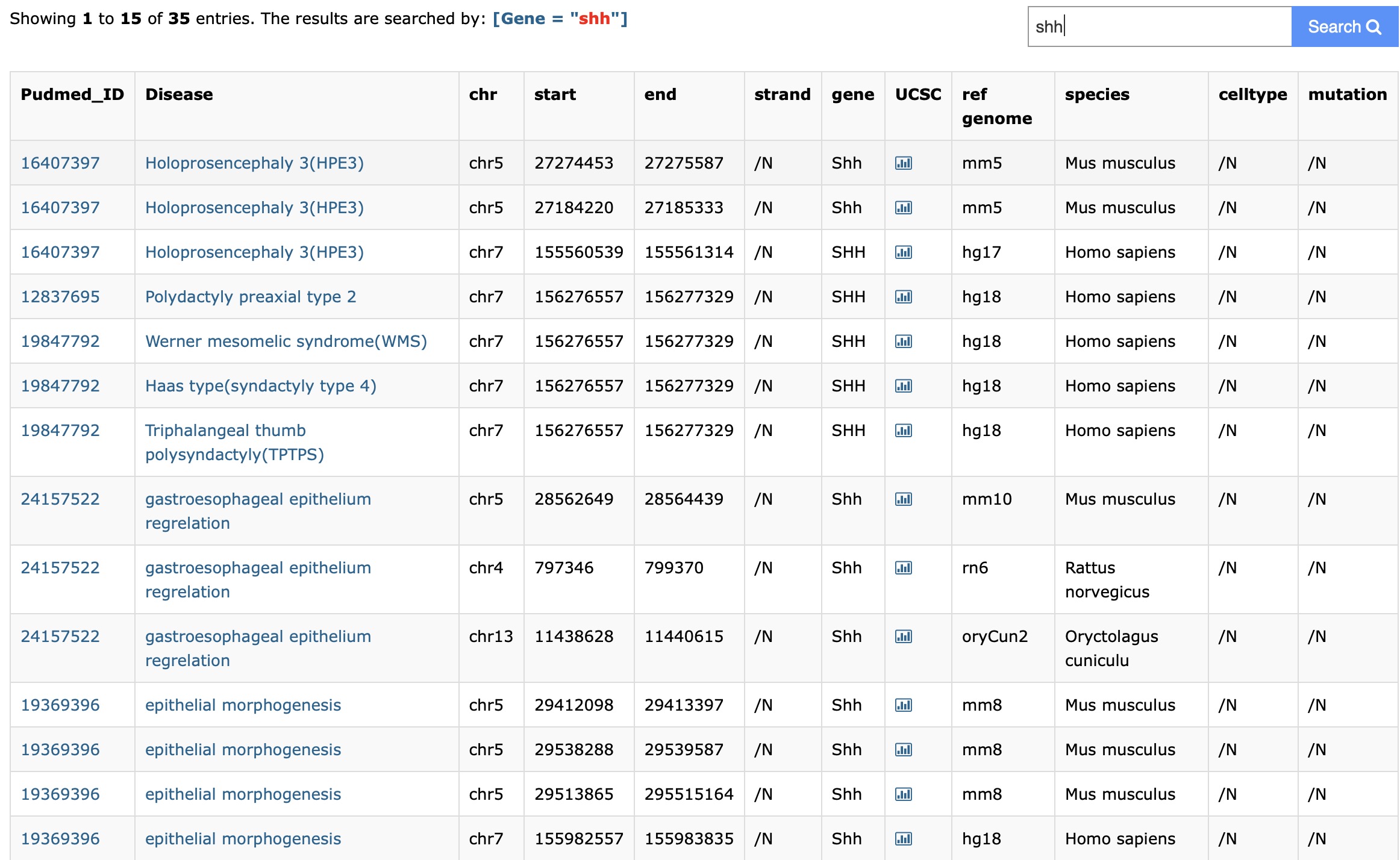
Users can select the gene symbol in the search box in the "By Gene" module. Then the database will return some enhancer-disease interactions, which are associated with the gene. Furthermore, users can export the search result using export button.
First, select the gene symbol you interested at the top right. Then you get your result and the search constraint will display at the top:

Users can select the disease name in the search box in the "By Disease" module. Then the database will return some enhancer-disease interactions, which are associated with the disease. Furthermore, users can export the search result using export button.
First, select the disease name you interested at the top right. Then you get your result and the search constraint will display at the top:
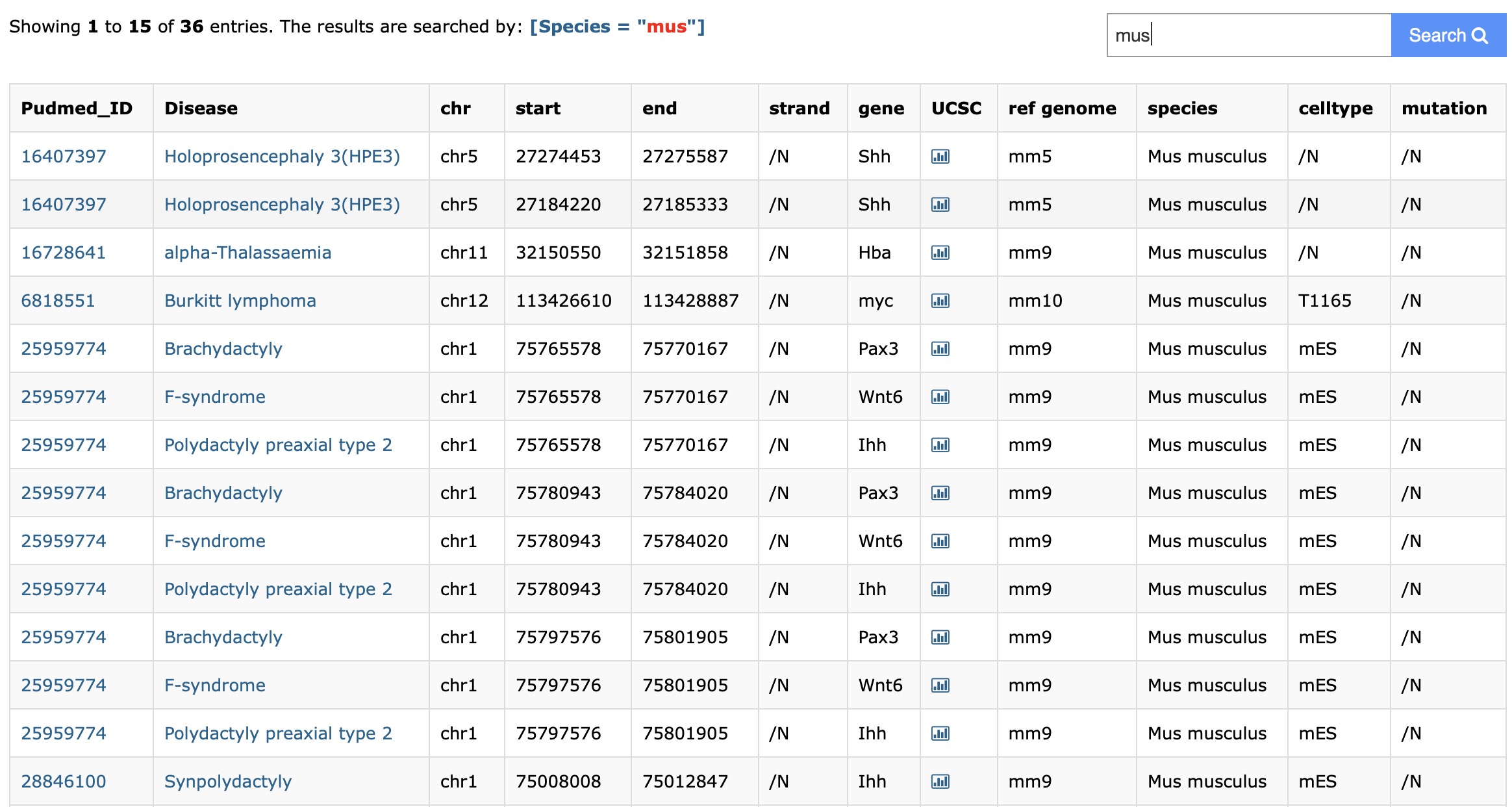
Users can select the species in the Dropdown menu in the "By Species" module. Then the database will return some enhancer-disease interactions, which are validated in the species. Furthermore, users can export the search result using the export button.
First, select the species you interested at the top right.Then you get your result and the search constraint will display at the top:

Enhancer-disease dataset means that the enhancer-disease are the potential interactions in the reference papers and are experimental verified. Epigenomic annotation dataset means that the each enhancer-disease are annotated with 871 DNase-seq experiments.
Users can download interactions from "Search" module. Users can enter or select an enhancer location (chr, start, end) or gene/disease/species name in the "Search" module. Then the database will return some enhancer-disease interactions. For all these interactions, the users can link out to original reference paper in Pubmed. Furthermore, the database provides a txt file containing all columns of every queried interaction for download.
First, enter the search constraint you are interested in. Then you get your result and the search constraint will display at the top, and click the export button at the bottom:
 We provide "bulk download" for all enhancer interactions in the "Download" module, and users just click the download button in the different datasets and they will get all the interactions they want. Wo also provide epigenomic annotation for all enhancer-disease interactions in the "Download" module.
Click the dataset you are interested in and download:
We provide "bulk download" for all enhancer interactions in the "Download" module, and users just click the download button in the different datasets and they will get all the interactions they want. Wo also provide epigenomic annotation for all enhancer-disease interactions in the "Download" module.
Click the dataset you are interested in and download:
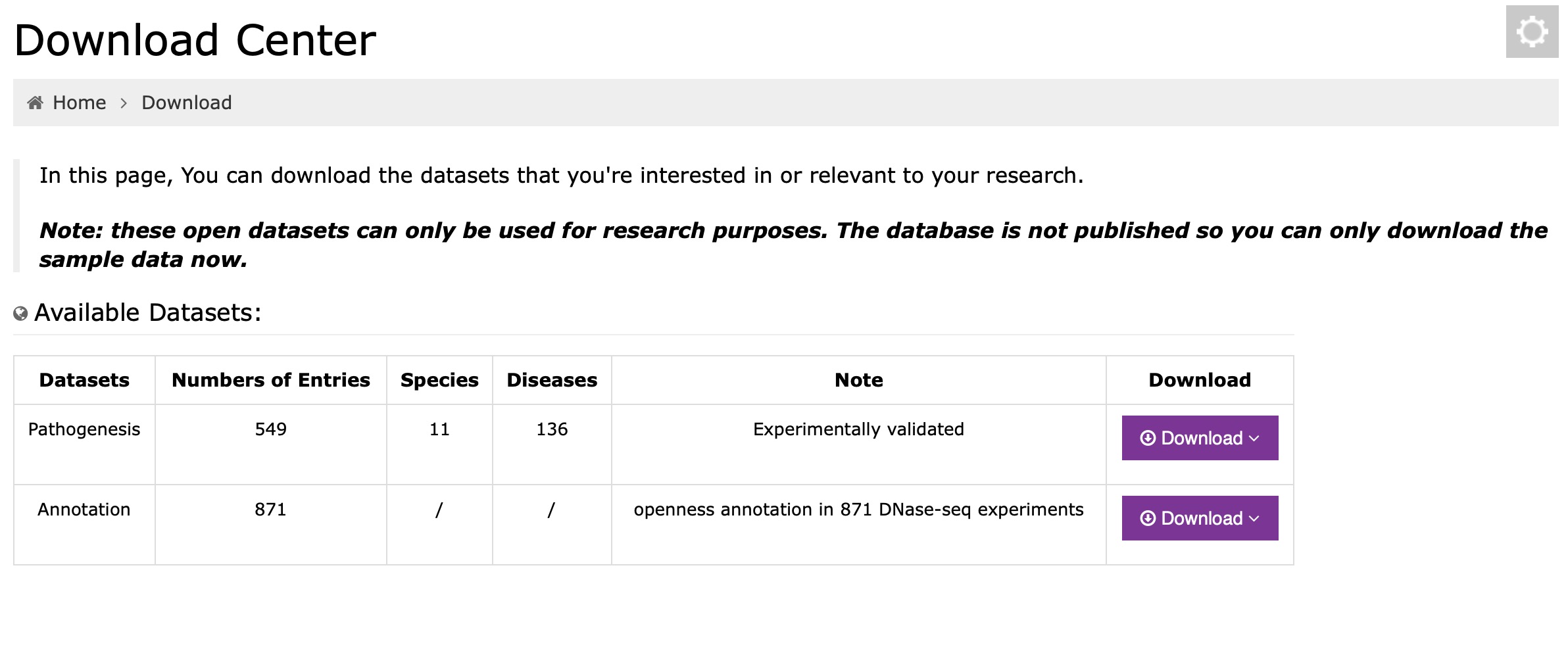
 We provide "bulk download" for all enhancer interactions in the "Download" module, and users just click the download button in the different datasets and they will get all the interactions they want. Wo also provide epigenomic annotation for all enhancer-disease interactions in the "Download" module.
Click the dataset you are interested in and download:
We provide "bulk download" for all enhancer interactions in the "Download" module, and users just click the download button in the different datasets and they will get all the interactions they want. Wo also provide epigenomic annotation for all enhancer-disease interactions in the "Download" module.
Click the dataset you are interested in and download:


